An Extensive Guide on What is Malware in Cyber Security

Have you ever suffered from malware attacks? If so, this blog is for you.
If not, to start any e-commerce site or project development, knowing what is malware in cyber security will be helpful to protect your businesses.
In the ever-evolving world, as technology has developed, cybercrime has grown. Moreover, cybercriminals have now developed very sophisticated cyber crimes. Cybercriminals use malicious software on vulnerable computing systems to achieve malicious purposes. This is why the battle against malware has been an ongoing process since the advent of technology.
However, to counter malware attacks, you need to understand the term malware well. In this blog, we will illustrate what is malware in cyber security, types of malware, and malware detection, prevention & removal strategies with examples.
What is Malware in Cyber Security?
Malware in cyber security refers to any intruding file, code, or software that is developed & delivered by cyber criminals over a network that infects, steals, or destroys a victim’s computer, computer systems, or sensitive information.
Numerous types of malware, such as viruses, Trojans, adware, spyware, and ransomware, can infect the computer system. An eminent example of a malware attack is the WannaCry Ransomware Attack.
Purpose of Malware: What is Malware Used for?
The primary purpose of malware is to cause devastation and steal confidential data or resources for monetary gain. Attackers create & develop malware as harmful software to attack your computer system or network. Therefore, attackers use this for the following objects based on their types and capabilities:
- Disruption: Control the victim’s computer system to disrupt using malicious code.
- Destruction or Intrusion: Send spam from the infected system to the target systems.
- Vandalism & monetary gain: Verify the infected user’s local network.
- Steal Computer Resources: Use malware in your computer system & network to steal confidential data.
Types of Malware: Malware Examples in Cyber Security
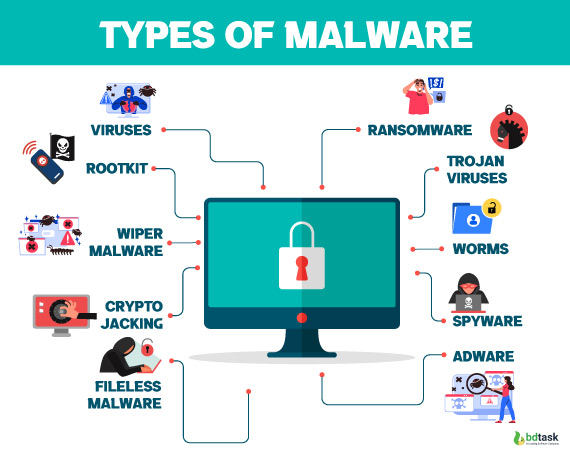
Malware is a comprehensive term for all types of cyber threats in cyber security. If your computer or other devices are acting weird or not responding, it may be a malware attack.
However, to know well what is malware in cyber security, you should know well about malware types and examples. Here are list of malware, malware examples and how they spread:
Ransomware: Ransomware is the most dangerous type of malware in cybersecurity. Unless a ransom is paid, it uses encryption to disable users or organizations from owning their data and systems. There is no guarantee that victims and organizations will get a decryption key that will function properly after the ransom is paid.
Ransomware Example: In 2023, global ransomware attacks increased 95% over 2022. RobbinHood, a ransomware attack has cost more than $18 million and continues to accrue. Various types of ransomware are WannaCry, Cryptolocker, Ryuk, Petya and many more.

According to a source report of cyberint.com, a picture of the top ransomware-targeted countries in Q3 2023.
Trojan Viruses: A Trojan disguises itself as an innocent program hiding in apps, games or email. Once a user downloads the trojan, it can attack a system and allow attackers to gain control of the user's device.
Trojan Example: A complex banking trojan named Emotet, is very hard to fight against. What is malware in cyber security can be described by its persistence, evades signature-based detection and includes spreader modules that help to propagate. According to a US Department of Homeland Security alert, Emotet has cost govt up to $1 million per incident to remediate.
Viruses: Malicious software can inject viruses that contain malicious code into an application and computer. The malicious code can execute when the application runs to cause system damage, steal data, corrupt files, launch ransomware attacks and much more.
Viruses Example: Viruses depend on the host to download them.
Worms: Worms are similar to viruses. They are self-replicate and target vulnerabilities in operating systems, but they do not need to be attached to another application. After being installed into networks, they can launch various attacks, including distributed denial of service (DDoS). They may obtain access through several ways, such as backdoors built into the software, unintentional software vulnerabilities, or flash drives.
Worm Example: A worm attack, Stuxnet, was introduced into Iran's environment through a flash drive by the US and Israeli intelligence forces.
Spyware: Spyware is a type of malware that enables actors to collect information about users' confidential data, payment details, and credentials. It can affect desktop applications, personal information, and mobile phones because it can operate in a critical and mobile app.
Spyware Example: An incident can be described as an example of a spyware attack. DarkHotel used various types of malware to access sensitive information and passwords of targeted government and commercial leaders using hotel WIFI.
Adware: Adware is a form of spyware. But it doesn't require software installation on the computer nor capture keystrokes. It allows attackers to track the user's surfing activity, behaviour pattern, and interests without consent.
Adware Example: Fireball, an adware attack, infected 250 million computers and devices in 2017. This attack aims to hijack browsers to change default search engines and track web activity.
Cryptojacking: Cryptojacking is used unauthorizedly on victims' devices without their consent to track their computing resources to generate cryptocurrency. This malware can affect the system's stability, become slow, and cause higher electricity bills for the victim.
Cryptojacking Example: The Romanian hacker group uses default or stolen credentials and exploits vulnerabilities to launch a DDoS attack or mine Monero currency to compromise with Linux servers and the Internet of Things (IoT).
Wiper Malware: what is malware in cyber security refers to a type of malware named Wiper malware. Wiper malware aims to damage user’s data and computer systems. Generally, threat actors use this malware to cover up traces left after the devastation. Also, they intend to send political messages or hide their illegal activities after data exfiltration.
Wiper malware Example: A set of malware dubbed WhisperGate was reportedly deployed against Ukrainian targets on 15th Jan,22. This incident contained three components deployed by the same adversary: a malicious bootloader that corrupts detected local disks, a file wiper, and a Discord-based downloader.
Rootkit: This malware is software injected into applications, firmware, operating systems, or hypervisors. For this reason, the actor can access the remote control of the user’s computer. Besides, attackers deliver malware to other devices through phishing, malicious downloads, and attachments.
Rootkit Example: When users unintentionally download a fake VPN app, Zacinlo infects systems. After installation, Zacinlo conducts a security issue for competing malware and tries to remove it. It opens an invisible browser and interacts with content like a human would by scrolling, clicking, and highlighting.
Fileless Malware: Fileless malware denies software installation on the operating system; instead, it changes files in the operating system. It makes native files into malicious functions challenging to detect because files are recognized as legitimate, such as Powershell or WMI. This type of malware is ten times more successful than traditional malware.
Fileless Malware Example: Astaroth is a fileless malware that spams users with links to an LNK shortcut file. A WMIC tool and multiple legitimate Windows tools were launched when users downloaded the file. These tools download extra code that was executed only in memory. However, attackers downloaded and ran a Trojan to steal credentials. Then, they uploaded them to a remote server.
How Can Malicious Code Cause Damage?: Understand with Example
Malicious code causes immense damage to devices and systems. Do you know what malicious code is in cyber security and how it damages the system? Malicious code refers to causing back doors, security breaches, information and data theft, and other potential damages to personal resources and computing systems.
Threat attackers design this code to cause damage, steal, and make unwanted changes to the computing system.
Moreover, malicious codes allow threat actors to automate their attacks. The critical fact is that malicious codes can even spread, replicate, and cause damage on their own.
However, this code can infect any device using a computer to operate, such as:
- IoT Devices- in-vehicle infotainment systems (IVI)
- Computer Network Devices like routers, modems, servers.
- Traditional Computer devices like desktops, mobile phones, laptops
Hence, attackers use malicious scripts to breach trusted parts of computer systems. This malicious scripted code may need computer actions or human actions to operate autonomously following this structure:
- Investigate and probe for any system’s vulnerabilities
- Expose the computer systems to malicious code
- Program by written code to exploit vulnerabilities
- Conduct the code through a related program or on its own.
Therefore, malicious code can lead to any of the following causes:
- Data Corruption
- Extortion and Ransom
- Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS)
- Private Information and Credential Theft
- Nuisance and inconvenience
Example of Malicious Code: Common malicious examples include worms, spyware, Trojan horses, adware, backdoor programs, and logic bombs. Clicking on a fake email link or attachment or surfing infected websites can cause malicious code to enter the system.
How to Detect the Symptoms of Malware?
If your device acts abnormally such as slow performance, unexpected freezing or crashing, homepage unintentionally changes, strange error messages, annoying pop-ups or browser redirects, these are all symptoms of malware infection.
Follow this guideline to identify the symptoms of malware infection and take precautions against malware.
- Slow Performance
- Unwanted Crushing or Freezing
- Browser redirects
- Annoying pop-ups
- Disable System tools
- Fake Virus Alert
- New Browser Toolbars
- Diminished Storage Space
- Changes in Security Settings
- Randomly Homepage Changes
Which of the following is not an example of malware?
Keyboard, Human ware, and bugs are not malware because human beings wear these. Worms, viruses, spyware, and adware are computer-related and are called malware.
How to Get Rid of Malware?
The best solution to eliminate malware is to use malware protection technology. Individuals and organizations should use different types of malware protection in cyber security, including signature-based malware detection, behavior-based malware detection, and sandboxing. Using antivirus software on computers and mobile phones is a significant prevention to reduce malware attacks.
Hence, here are some ways to get rid of malware:
- Keep your devices & system Upgraded: Cyber actors always search for outdated and vulnerable software and systems to attack. So, ensure your devices and systems are updated regularly.
- Keep your antivirus Upgraded: Keep anti-virus tools to prevent malware. Also, make sure your anti-virus is updated. Must use anti-malware software, such as Avast, Norton 360, ExpressVPN, NordPass, ZoneAlarm, etc., to prevent malware.
- Use Legitimate Software: Normally, malware spreads via traditional software tools. So, ensure your operating systems and software are running on the latest version and that all patches are installed.
- Verify External Emails: Do not click suspicious links in an email that appears from your known connection to get access to your password or private information.
Important Tips to Avoid Downloading Malicious Code
We want to give you some tips to avoid downloading malicious code:
- Avoid using illegitimate software: You should allow only pre-approved software on the company's computers and servers because malware is generally delivered via compromised versions of popular software tools.
- Educate & train your users on malware attacks: You should adequately educate and train your employees to avoid downloading social engineering schemes like phishing attacks. Moreover, train them to report suspicious communication or system behaviour to the security team.
- Use threat intelligence & security analytics: Always monitor network traffic to understand your network, whether as usual or not. Use real-time threat intelligence to gain extended visibility into threats affecting your network.
- Awareness: You should conduct a security awareness campaign in your organizations about how to prevent malware infections. Also, based on how to detect malware infections and what to do after detecting a compromised system.
How to Remove Malware?: Follow Step-by-Step Guidance
What is malware in cyber security significantly refers to removing malware and protecting your devices, too. So, how should a company handle a ransomware attack, the impressive solutions against malware to protect systems and devices are:
- Use malware protection software: Keep monitoring your network systems. Use robust malware protection software, and you can also use free malware removal for Android. To avoid entering malware, some anti-malware software examples are Bitdefender, Malwarebytes, McAfee, Trend Micro, Kaspersky Antivirus, etc.
- Run Phishing Simulations Regularly: Try to run phishing simulations regularly to provide advanced skills to your employees in identifying phishing attempts. Regular checks help maintain awareness and identify and remove malware.
- Scan your device & system: You can scan your devices with a malware scanner. It can delete anything that might seem like a problem, and you have to restart your devices for these changes.
- Try to recover your operating System: First, go to your device manufacturer’s website to recover your system. Follow this step to step: control panel> Search recovery box> type recovery> select recovery> open system restore. You will get back a lot of data if you can successfully recover your system to alternate reinstalling your operating system. Then, you can go back to the previous steps to ensure you have removed the malware.
- Refix or reinstall your operating system: To reinstall the operating system, follow the device settings> select update & security> Click recovery in the left menu panel> under reset this PC, click Get Started> choose whatever files you want or remove> Finally click reset. It is the safest way to clean your infected device. But the saddest fact is you will lose all the stored data that needs to be backed up.
What is the Best Protection Against Malware?
Here are some of the best malware protection in cyber security:
- Patch and Update Software: Always keep your systems upgraded and secured. Further, use the best anti-malware software for Best malware protection in cyber security.
- Use Firewall and Security Software: Use firewall and security software to block malicious traffic entering your network. A firewall can help defeat outgoing communications to hackers if malware enters a network device.
- Deploy Advanced Email Security: Most ransomware infections are approached from email attachments. So, you should instrument a layered security approach that can protect your end users as well as company-sanctioned file-sharing solutions from cyber threats.
- Use Strong Password: You must ensure all users use and change solid and unique passwords regularly. Besides, you can use a password manager to make this topic more accessible for users to remember & secure their passwords.
- Backup your data and resources: Keeping a Backup of your systems and resources is the best practice to protect against malware. If your system or organization is attacked by network-based ransomware, worms, or other malware, you will operate generally with your backups.
The Verdict
In conclusion, what is malware in cyber security doesn’t only require understanding the diversity of malware. But also requires the methods of infection and prevention and prudent strategies to protect our devices, networks, and credential information.
As cybercrime is rising, it is hazardous for the whole world. So, you should take significant steps and consult with cyber firms for cyber risk to protect your system & network of your organizations.












