Software Development Life Cycle: From Idea to Execution

Software Development Life Cycle, or SDLC, is a process to plan, design, and develop a complete software application. It is a common term used in the software industry. SDLC provides step-by-step software development methods.
Through the process of the Software Development Life Cycle, developers can easily build high-quality software solutions. Moreover, SDLC helps software development companies or software service providers to construct software that can meet the customer demands. It has different phases and models.
Here, we will explore every stage involved in software development and illustrate the necessity of software in every industry. So, go through the article and explore the Software Development Life Cycle in detail.
What is the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)?
The software development life cycle is a construction process of software. The SDLC model involves every aspect of software, such as planning, designing, developing, testing, and maintaining.
Moreover, SDLC also provides information on how to improve the quality of software. Following the models, software engineers can reduce the risk associated with the software development.
The software development life cycle (SDLC) is also considered an application development life cycle. And the importance of SDLC in software development is very high. It helps to architect the software prototype before writing the codes.
Why Should You Go For a Software Development Process Lifecycle?
The software development lifecycle roadmap itself describes the development process of software. However, developing efficient and qualityful software is challenging.
It involves a lot of stress, such as repeatedly changing requirements, searching & choosing the best suitable technology, and cross-functional collaboration between multiple departments. Moreover, the software application development lifecycle (ADLC) follows systematic framework management.
Therefore, at every stage of software development, a developer has to cross-check with the client; even though this process is time-consuming, it is still an effective way to fulfill the requirement.
Reason For Choosing SDLC Model:
- Better client satisfaction
- More visibility to the stakeholders
- Well-organised planning, assessment, and schedule
- Less risk and accurate cost estimation
- Improved software development outcome
7 Dynamic Stages of Software Development Life Cycle
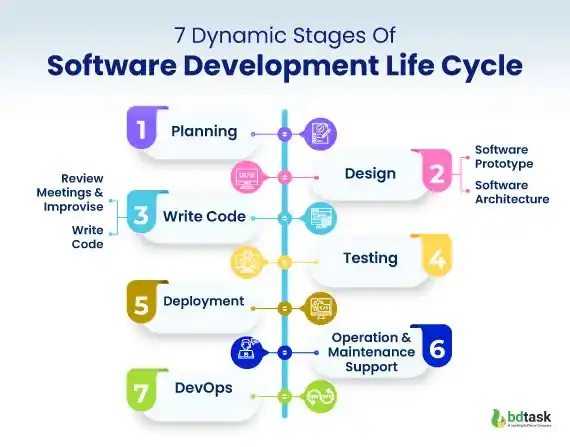
The software development life cycle goes through different phases. Each phase contains a specific plan. And the plan describes the details of the software development plan. SDLC modes also help the developers to improve the software applications. Maintaining a chronology software development roadmap helps to be strict with business logic and time schedule.
Here, we will go through the phases of the entire SDLC model and its graphical representation.
Phase 1: Planning
Planning is the first and most important part of software development. A well-planned project can ensure an effective output within the budget and timespan. However, the planning phases can be in different portions. One is requirement gathering, and another is brainstorming and analysis. Let's get into more details.
-
Requirement Collection
It's usually considered a first meeting with a client, or it is an introductory meeting with potential customers.
Conventionally, this meeting is conducted between the senior developer and the head stakeholder of the company.
Below I have shared a chronological list of topics both parties will discuss in the first meeting:
- Introduce themself
- The head stakeholder will give a brief introduction about the organisation.
- Senior developers will give briefs about themselves and past achievements.
- Head stakeholders will start briefing about the projects, initial requirements, overall goal, intention, buyer persona, and vision.
- Senior developers will note down all the requirements and clear out any raw confusion from the client.
- Also discussed is the necessary quality assurance, risk & difficulties associated with the project.
- The head stakeholder will share all the software requirement specifications (SRS) documents with the senior developer for the application development's sake.
- In the end, the head stakeholder will share their budget and the time barrier for the project.
-
Feasibility Study: Brainstorming & Analysis
This part of the phases can only be started after conducting the first meeting with the client. In this second stage of SDLC, a senior developer will sit with his team and divide all the work among the team.
Besides, I will also brainstorm the requirements, examine the software requirement specifications (SRS) and identify the best solutions to create the software.
In short, developer planning is to sketch down an initial demographic transformation based on the user requirement and software requirement specifications. And discuss which technology, design, programming language, and framework to use to get the best outcome.
3 Types Of Design, Which Can Be Sketch At The Initial Stage
Architectural Design: Abstract Version Of The System
High-level Design: List Of Modules Of The System
Detailed Design: Logical Structure Of Each Module and how those will be linked with each other.
Disclaimer## All this brainstorming, initial sketching, and software requirement specifications will be needed while writing the code.
Phase 2: Design
When the planning and feasibility analysis is complete, now it is time for designing. In this phase, the team creates an overview of the software applications. The design phase can be described as having two distinct parts: software prototype and software architecture.
-
Software Prototype
Constructing a practical software prototype is an essential part of the software development roadmap. A software prototype is a perfect visualisation of how the original software will perform. Also considered to be the best way to evaluate, test, and validate it from users.
Additionally, designing a practical software prototype reduces the risk of the original project. Even though the software prototype doesn’t include all the features, it focuses on all the essential and complicated elements that need to be cross-checked by the clients.
Point Out Reason For Building Software Prototype Before The Original Application:
- An early stage of software development is the best time for feedback, validation, and evaluation
- Aware About Your Progress
-
Software Architecture
Software architecture is crucial in the "designing phase" of software development life cycle methodologies. Software Architecture is considered a fundamental part of the software and helps develop a structured software solution.
Mainly, software architecture marks out how the modules of software are assembled, their integration, and their synchronisation with each other. In short, software architecture provides business logic and how the process will work in a software application, which later hugely assists the developer team while coding.
Phase 3: Writing Code or Developing Product
After designing, the developing phase starts. It is one of the most important parts of software application development. However, in the product development phases, developers write the codes and develop the applications. Here, we will describe the details about building or developing the products.
-
Review Meetings & Improvise
The software prototype review meeting will be important for both the head stakeholder and the developers. Because, this review meeting not only gives developers the chance to showcase the software demonstration, but they also get the opportunity to collect feedback and validity from the clients.
In addition, the developer and client will discuss the issues, difficulties, and confusion faced while constructing the software prototype.
After the meeting ends, the senior developer will sit with the development team and discuss all the issues, feedback, & changes suggested by the clients. And it's the senior developer's responsibility to ensure all the discussed problems get fixed and conduct a quick follow-up meeting with the clients.
-
Write Code
Once the software prototype has been shaped, the developer can start writing the code. In the phrase, developers will begin constructing the software system using the suggested programming language.
Usually, the coding part is divided into different sectors for instance; units, modules, UX/UI design, frontend & backend, and also assigned to multiple developers for rapid output. In short, this phrase is the most critical phase of the software development life cycle.
Moreover, in this phrase, developers strictly follow the predefined coding guideline. And use the following programming tools: compilers, interpreters, debuggers, and programming languages such as C, C++, Pascal, Java, or PHP.
Phase 4: Testing
The complete cycle of software development life cycle methodology and software testing life cycle (STLC) will identify & measure whether or not the raw intended thinking of the client matches with the developed one.
The quality assurance, also known as the "testing team," will start with their testing program by checking the entire system's. It includes, functionality, user experience, security check, CTA buttons, links ups, parents/child modules, business logic, and their process.
In addition, the quality assurance team will also track down the bugs, irrelevant parts, or defects and will notify the developer. They will also do both manual & automated testing based on tools and scripts. And this testing session will continue till the developer improvises all the bugs, and the system gets stable, operating just like the client requires.
Phrase of Software Testing Life Cycle (STLC)
- Requirement Analysis
- Test Planning
- Test Design
- Test Environment Setup
- Test Execution
- Test Closure
Phase 5: Deployment: Moment of Truth
Deployment stages of SDLC start just after the developer completes fixing the bugs the quality assurance team found. And with the client's permission, the senior developer will release or make the final software live.
Software deployment processes can be both long & short, depending on the nature of the software. One essential part of deployment is ensuring all the functions and business logic are working perfectly.
Phase 6: Operation & Maintenance Support
Once the final software application is live, the end user will start using the software. However, while using it, users might discover new bugs, and that's when developer support will be needed.
3 Types Of Maintenance Support Will Need After The Deployment Stage
- Bug fixation
- Software upgradation
- Enhancement
- Add ons development
Phase 7: DevOps: End-Game of SDLC
DevOps is considered to be the last phase of the software development life cycle methodology that increases speed, efficiency, and output.
DevOps methodology minimises the number of steps in the software lifecycle by creating a collaboration between the developer and the operation team.
DevOps is a new way of development, where a cultural shift has significant implications for both the teams and the organisation.
In the past, developers were only responsible for their work, but now developers do more than just develop every step of the SDLC.
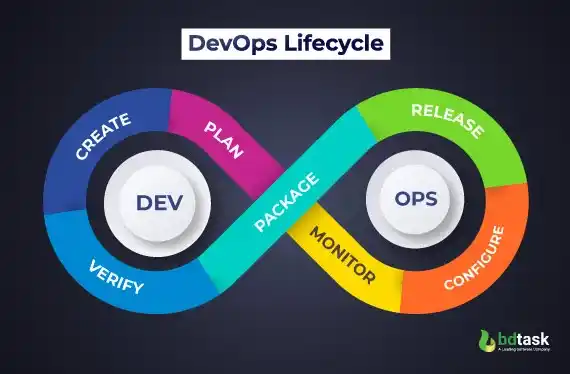
Fig: DevOps Lifecycle
Benefits Of DevOps
- Improve the page speed
- Improved collaboration between developers and operations teams
- Rapid deployment
- Improve Quality and reliability
- Improve security issues in every SDLC phrase
6 Types of Software Application Development Lifecycle
SDLC models not only help develop the software but also show developers a path to construct it in an organized manner. Each SDLC model follows a series of unique phases or different chronological orders, thus ensuring success in the step of software development.
But there are some common SDLC models that are more frequently used and widely popular. Here, we will describe the most popular types of SDLC models.
1. Waterfall Model
The waterfall model is also called the linear sequential model, and this model is one of the most commonly used models in SDLC.
Brief Explanation of How the Waterfall Model Works:
First, the whole development process will be divided into multiple predefined phrases. The most important part of the waterfall model is that each phase should be completed before starting the next phase.
And each phase has its own responsibility and duty to perform. Any overlap between the phases is impossible in the waterfall model.
Which Type Of Application Development Project Is Appropriate For the Waterfall Model:
- Requirements will not change frequently
- The application will be straightforward and short
- Requirements will clear
- The environment will be stable
- The technology and tools used are not upgraded
- Resources are available and skilled
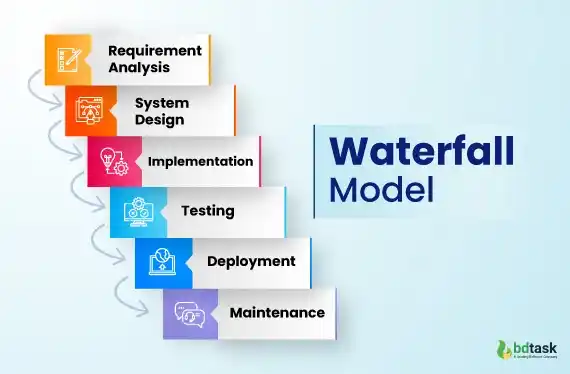
Fig: Waterfall Model
2. Iterative Model
The iterative software development model is also considered to be part of the software development life cycle.
Brief Explanation of How Iterative Model Works:
The iterative model starts by dividing the software system into multiple sub-functional, and each Iterative process will be developed separately using the same SDLC process (requirements, design, coding testing, and support).
And the SDLC process will continue to repeat until each function gets properly fixed and all requirements get adequately fulfilled. Each phase is the improvement version of the previous software release, in the case of functionality, and business logic.
In short, the first version of software product increment fulfills the core & basic requirements.
The second version of the software product increment will fulfill the other supplementary features to make it more advanced than the previous one.
In the third version of the software product increment, the final product will be presented to the client, evaluated by the clients, & ready to make it live.
Which Type Of Application Development Project Is Appropriate For Iterative Model:
- The requirements of the system are very clear
- There is a demand for an early product release
- software developer team is not that advanced
- Highly advanced features and objectives are involved, such as banking software
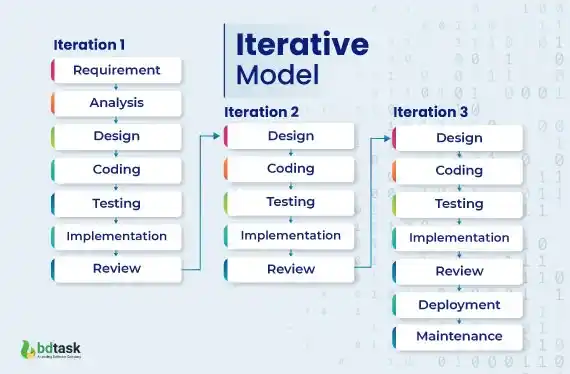
Fig: Iterative Model
3. Agile Development Model
The agile software development model is quite similar to an iterative model.
Brief Explanation of How Agile Development Model Works:
In the agile development model, the application development process will continuously operate the "planning", "learning", "development", "improvement", and "deployment" together. In short, both the development and testing processes will have to work simultaneously.
The agile development model is considered one of the most uncomplicated and effective software development processes that assist in constructing a business's intended vision into reality. However, the Agile model has some limitations but is also very popular in the software industry.
Which Type Of Software Development Project Is Appropriate For the Agile Development Model:
- Team collaboration and discussion about programs and tool
- Where the customer has a frequent chance and in the urgency of the software
- The project is flexible and has the opportunity to correct errors in the middle of the project
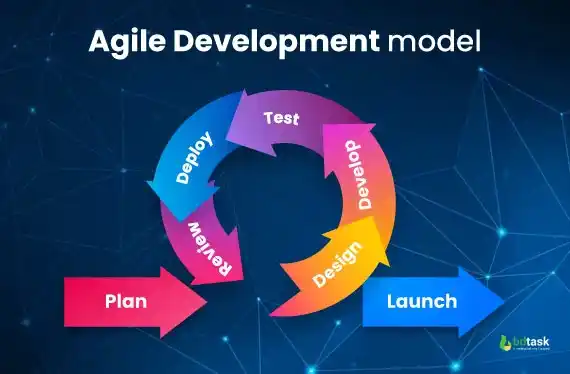
Fig: Agile Development Model
4. V-model
The V-shaped model is a highly structured model which follows two parallel development phases. One is called the verification phase, and another is called the validation phase, and both jointly end up in the coding phrase.
Brief Explanation of How V-Model Works:
The V-shape model is also known as the verification and validation model. The V-shaped software life cycle model is the extension version of the waterfall model, where both the development and testing processes operate consecutively in the stage of the development process.
The V-shape verification model indicates the practice of evaluating the software development process, and their primary purpose is to ensure the developer team meets all the requirements. This verification model includes steps such as:
- Business Requirement Analysis
- System Analysis
- Software Architecture Design
- Module Design
- Coding
Moreover, the V-shape validation model indicates the practice of dynamic analysis method and testing of the software functionality to ensure all the requirements match with the developed one. This validation model includes steps such as:
- Unit Testing
- Integration Testing
- System Testing
- Acceptance Testing
When To Use V-Shaped Model
- Run testing throughout the development process
- The testing process will be run in the parallel process
- Prevent defects rather than identifying and fixing them
- The left side in V shape model is the SDLC
- The right side in V shape model is the software test life cycle (STLC)
- The entire figure is like a V-shape, which is why it is called a V-shape model
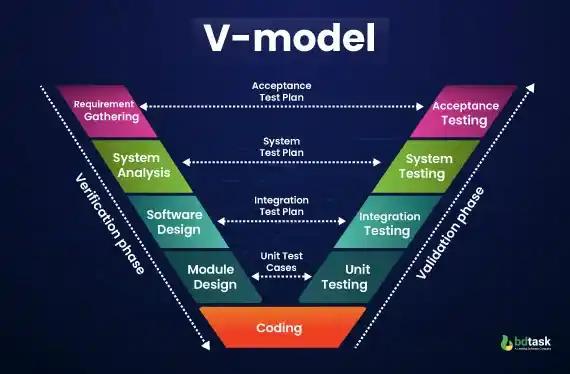
Fig: V-Shaped Model
5. Spiral Method
The spiral software development life cycle is a risk-driven SDLC process, thus a safety net for big and complex application systems. The spiral method combines two types: process model, waterfall model and iterative model.
What Is Spiral Model In SDLC
The spiral system development life cycle process operates just like waterfall model stages but with a little twist. When the spiral loop starts, it separates the SDLC life cycle stage into 4 different parts.
- Planning
- Risk Analysis
- Engineering
- Evaluation
And each part of software development in the spiral cycle starts with setting a small set of requirements to develop. As the spiral cycle moves to the following stages one by one, it will add different business functionality, modules, bug fixation, etc., till the application lifecycle framework is ready for production.
When To Use Spiral Model SDLC
- When the Client Ask For Frequent Updates On the Progress
- Software Project Is Large
- Software Project Requirements Are Unclear And Complex
- The client May Ask For Change Repeatedly
- High Budget Software Projects

Fig: Spiral Model
6. Prototyping Model
The software prototype model is a preliminary version of the software. And a software developer can only start constructing the software prototype when finishes gathering all the requirements of the clients.
This software prototype model in SDLC can only be constructed after gathering all the requirements from the client. The main purpose of building a software prototype is to create an early or demo model of a software project.
It helps the developer team to collect initial client feedback. The software prototype model is a demo version of the software, hence lacking a lot of functionality, process, and modules.
There are two ways to use this software prototype while developing the software:
- Developers will rapidly develop the software using the prototype model.
- Developers will follow the software prototype step by step and improvise it by adding different advanced features and functionality.
Following Steps To Follow To Develop A Software Prototype:
- Understanding the basic requirement of projects
- Develop the prototype model in SDLC
- Take feedback on the prototype from the clients
- Revise and improvise the prototype
When To Use Prototype Model in SDLC?
- Assist to bring a significant reduction in risk
- Help to reduce costs.
- Best fit the product to user needs and market requirements.
- Uncover key issues early and improvise them
- Accelerate sales cycles and early customer exposure.
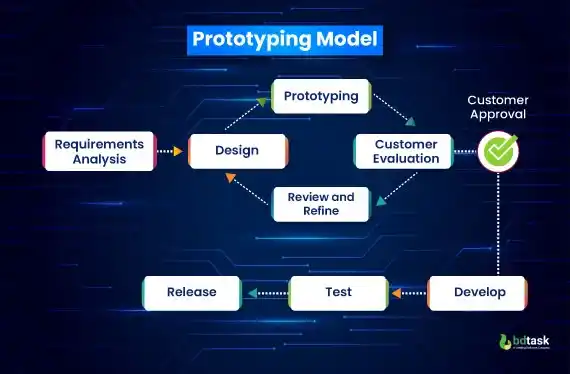
Fig: Prototype Model
Advantages and Disadvantages of SDLC
One of the major advantages of custom software development is that organisations can personalise their own application development system based on the requirements, needs, and operation standards.
And apart from this reason, there are other issues too, which help you decide whether or not an organisation should go with a custom software development service.
Advantage
- Well organised & structured software development plan
- Less chance of any steps getting overlooked
- Chance to identify & improve bug issues while developing
- Software development within budget
- Guaranteed to meet the need of the end-user
- Better collaboration between the teams and clients
- Efficient use of resources
- Assurance of on-time project delivery
- Flexibility to choose the SDLC methodology that works best for you
- Develop software documentation
- SDLC encourages open opportunities for application improvement from client feedback and evaluation
- Organisations can maintain the industry standard with custom software development services
- Multiple stages of quality assurance: for instance, testing, validation, verification and bug fixing
Disadvantage
- It is challenging to accommodate the changes at the last hour
- Time-consuming and costly
- Huge risk of getting delayed
- Too much focus on documentation rather than working on software development
- Massive miscommunication between the developer and clients
- Too much time & resources are spent on planning & documentation.
- If it uses a waterfall model, any problems encountered later might raise the cost and risk of delay.
- SDLC is not that suitable for agile development methodology.
- SDLC strategy might not be suitable for all types of software, especially those that need frequent updates
3 Types Of Lifecycle Management Methodology (LMM)
Lifecycle management is important. Basically, the lifecycle management is actually the development process of software. Every developer follows common lifecycle steps while developing software.And even though there have been 3 different life cycle methodologies, all 3 follow the exact SDLC life cycle phase.
Here, we will discuss the three types of lifecycle management methodology.
1. System Development Lifecycle
Basically, the system development life cycle is another term for software development lifecycle roadmap. Like SDLC, the system development life cycle starts by gathering client requirements and stops at maintenance phrases.
Typically, a system development life cycle is developed by maintaining a combination of hardware and software components and solving a complex problem.

Fig: System Development Life Cycle
2. Custom Software Development Life Cycle
Another dynamic application development process is the custom software development life cycle. In this lifecycle management method, the whole process will conduct in the following chronology:
- At first, the client will contact with any top software company or IT service provider company
- Share their requirements
- Developers will brainstorm & analysis
- Negotiation of time & budget
- Design a Prototype
- Construct A Architecture
- Client Review Meeting
- Testing & Improvising Solution Deployment
- Writing the Code
- Maintenance Support
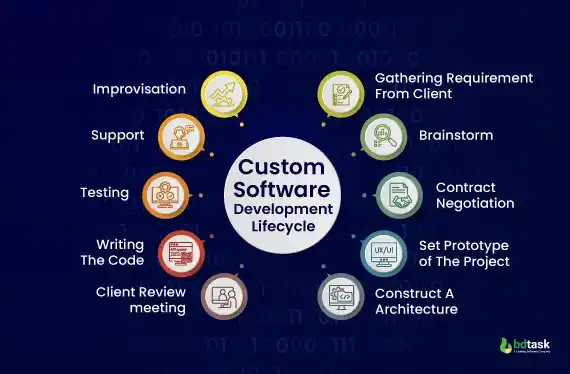
Fig: Custom Development Life Cycle
3. Application Lifecycle Management
The application lifecycle management (ALM) process is quite similar to the SDLC. And just like the SDLC phase, the ALM model starts with gathering clients' requirements and ends with maintenance & support.
An integrated application lifecycle management process because it brings together all the software departments, for instance, developers, analysts, & testers, to achieve the business goals.

Fig: Application Lifecycle Management
Application Lifecycle Management Tools
- Project Management
- Requirements Management
- Source Code Management
- Test Management
- Real-Time Chat Support
- Project Portfolio Management
- Visualization Tools (Charts & Graphs)
Conclusion
Most software development companies or mobile app development companies follow 7 to 10 software development roadmaps. The software development life cycle starts with gathering the software requirement from the client and ends with providing after-sale maintenance support to the client.
However, a developer's contribution is not just by handing over the software projects to the clients. Instead, they also have to give time to fix all the bugs, security issues, etc. So, every software service provider company must go through the SDLC model to meet the user expectations.










